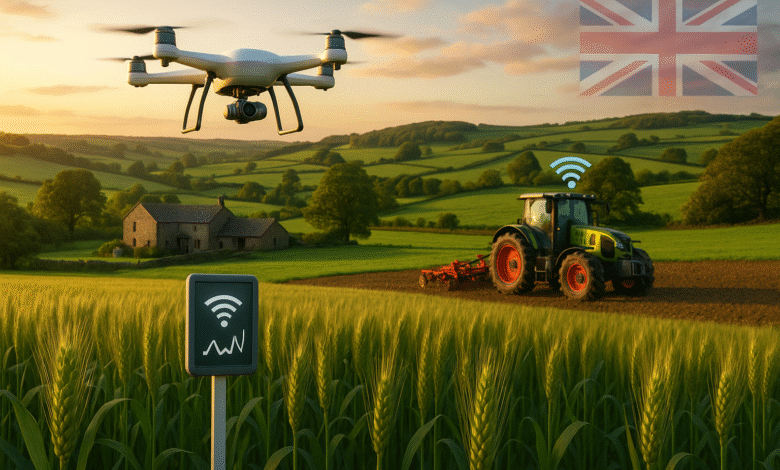
The farming landscape in Britain is changing fast. Technology is helping farmers grow more food while using fewer resources. Smart agriculture in Britain is not just a trend – it’s becoming the new normal for farmers who want to stay competitive and sustainable.
This revolution is happening right now across British farms. From the rolling hills of Scotland to the fertile fields of East Anglia, farmers are using smart technology to make better decisions. They’re saving money, protecting the environment, and producing higher-quality crops than ever before.
What is Smart Agriculture and Why Does Britain Need It?
Smart agriculture uses modern technology to help farmers make better decisions. It combines sensors, data analysis, and automated systems to create more efficient farming methods. In Britain, this approach is solving many challenges that farmers face today.
British farmers deal with unpredictable weather, rising costs, and pressure to reduce environmental impact. Smart agriculture in Britain offers solutions to all these problems. It helps farmers use water, fertilizers, and pesticides more efficiently. This means less waste and better profits.
The Internet of Things (IoT) plays a huge role in this transformation. IoT devices collect real-time data from fields, animals, and equipment. This information helps farmers understand exactly what’s happening on their land at any moment.
Weather patterns in Britain can change quickly. Smart sensors can predict when crops need water or when diseases might spread. This early warning system helps farmers act before problems become serious.
The Rise of IoT in British Farming
IoT technology is spreading rapidly across British farms. These connected devices are changing how farmers monitor their crops and livestock. The adoption rate is growing by 20% each year, making Britain a leader in agricultural technology.
Modern British farms use hundreds of different sensors. Some measure soil moisture, while others track animal health. GPS systems guide tractors with incredible precision. All these devices work together to create a complete picture of farm operations.
The cost of IoT devices has dropped significantly in recent years. What once cost thousands of pounds now costs hundreds. This price reduction has made smart agriculture accessible to smaller farms across Britain.
Connectivity has also improved dramatically. Rural broadband and 5G networks now reach most farming areas. This better internet connection allows real-time monitoring and instant data sharing between devices.
Key IoT Solutions Transforming British Agriculture
Soil Monitoring Systems
Smart soil sensors are revolutionizing how British farmers understand their land. These devices measure moisture levels, nutrient content, and pH balance throughout the growing season. Farmers can access this information instantly through smartphone apps.
Traditional farming methods required farmers to guess when crops needed water or fertilizer. Smart agriculture in Britain eliminates this guesswork. Sensors provide exact measurements, allowing farmers to apply resources only when and where needed.
These systems typically reduce water usage by 30% and fertilizer costs by 25%. For British farmers dealing with increasing input costs, these savings make a real difference to their bottom line.
The data collected helps farmers understand seasonal patterns in their soil. Over time, this information creates detailed maps showing which areas of fields perform best. Farmers can then adjust their planting strategies accordingly.
Weather Monitoring and Prediction
British weather is famously unpredictable, making weather monitoring crucial for farming success. Modern weather stations provide hyper-local forecasts that are far more accurate than general weather reports.
These systems combine data from multiple sources: satellite imagery, ground sensors, and atmospheric measurements. Machine learning algorithms analyze this information to predict weather patterns specific to individual farms.
Early frost warnings can save entire harvests. Smart systems alert farmers hours before dangerous conditions develop. This advance notice allows protective measures like irrigation or covering sensitive crops.
Rainfall prediction helps farmers plan field operations. Knowing when rain will arrive allows better timing for planting, harvesting, and applying treatments. This scheduling optimization increases efficiency and reduces equipment wear.
Crop Health Monitoring
Drones equipped with specialized cameras patrol British fields, capturing detailed images of crop health. These aerial surveys can detect problems invisible to the human eye, often weeks before symptoms appear.
Multispectral imaging reveals plant stress, disease, and nutrient deficiencies. Different light wavelengths show different aspects of plant health. Farmers receive color-coded maps highlighting areas needing attention.
Ground-based sensors complement aerial monitoring. They track growth rates, leaf temperature, and other vital signs. This combination provides complete crop health monitoring throughout the growing season.
Early detection of diseases allows targeted treatment. Instead of spraying entire fields, farmers can treat only affected areas. This precision reduces chemical usage and protects beneficial insects.
Livestock Management Systems
Smart agriculture in Britain extends beyond crops to include advanced livestock monitoring. Wearable devices track animal health, location, and behavior patterns. This technology helps farmers maintain healthier herds and increase productivity.
Individual animal monitoring provides insights impossible with traditional methods. Sensors detect early signs of illness, reproductive cycles, and stress indicators. Farmers receive alerts when animals need attention.
Automated feeding systems adjust portions based on individual animal needs. Pregnant animals receive different nutrition than others. Growing animals get increased portions automatically. This personalization improves animal health and reduces feed waste.
GPS tracking prevents livestock losses and monitors grazing patterns. Farmers can see which pasture areas animals prefer and rotate grazing accordingly. This management strategy improves grass quality and soil health.
Precision Farming Techniques in British Agriculture
Precision farming represents the practical application of smart agriculture principles. British farmers use GPS-guided equipment to plant seeds with centimeter accuracy. This precision ensures optimal plant spacing and reduces seed waste.
Variable rate application technology adjusts inputs based on field conditions. Areas with rich soil receive less fertilizer, while poorer areas get more. This targeted approach maximizes crop yields while minimizing environmental impact.
Automated machinery operates with minimal human intervention. Tractors can plant, cultivate, and harvest crops following predetermined patterns. This automation reduces labor costs and improves operational efficiency.
Real-time yield mapping shows exactly how much crop each part of the field produces. This information helps farmers understand which management practices work best. Over time, these insights lead to continuous improvement in farming methods.
Benefits of Smart Agriculture for British Farmers
Economic Advantages
Smart agriculture in Britain delivers significant financial benefits. Farmers typically see 15-30% reductions in input costs within the first year of implementation. These savings come from more efficient use of water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
Increased yields often accompany reduced costs. Precision farming techniques can boost crop production by 10-20%. Higher yields combined with lower costs create substantial profit improvements.
Labor savings represent another major benefit. Automated systems reduce the need for manual monitoring and routine tasks. Farmers can manage larger areas with the same workforce.
Equipment optimization extends machinery lifespan. Smart systems prevent overuse and schedule maintenance proactively. This approach reduces repair costs and equipment downtime.
Environmental Benefits
Environmental protection is a major driver of smart agriculture adoption in Britain. Precision application reduces chemical runoff into waterways. This protection helps preserve local ecosystems and maintains water quality.
Reduced tillage practices preserve soil structure and prevent erosion. Smart systems identify areas where cultivation is necessary and leave other areas undisturbed. This selective approach maintains soil health over time.
Carbon footprint reduction comes from multiple sources. Efficient equipment operation burns less fuel. Reduced chemical inputs lower manufacturing emissions. Improved soil health increases carbon storage.
Biodiversity benefits from reduced pesticide usage. Targeted application protects beneficial insects while controlling pests. This balance maintains natural ecosystem functions on farmland.
Improved Food Quality and Safety
Smart agriculture in Britain produces higher-quality food products. Precise nutrient management improves crop nutritional content. Optimal growing conditions enhance flavor and shelf life.
Traceability systems track food from farm to table. Consumers can verify the origin and production methods of their food. This transparency builds trust and supports premium pricing.
Reduced chemical residues result from precision application techniques. Smart systems apply pesticides only when necessary and at optimal rates. This approach minimizes residue levels in final products.
Food safety monitoring detects potential issues before harvest. Sensors can identify contamination risks and disease presence. Early detection prevents unsafe products from entering the food supply.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementation
Initial Investment Costs
The upfront cost of smart agriculture technology can be substantial. A complete IoT system for a medium-sized farm might cost £20,000-50,000. This investment can seem daunting for farmers with tight budgets.
Government grants and subsidies help offset these costs. The UK government offers various programs supporting agricultural technology adoption. These incentives can cover 30-50% of equipment costs.
Leasing options make technology more accessible. Many companies offer equipment rental programs. Farmers can start with basic systems and expand gradually as benefits become apparent.
Return on investment typically occurs within 2-3 years. Cost savings and yield improvements usually cover initial expenses quickly. Long-term benefits far exceed startup costs.
Technical Complexity
Modern farming technology can seem overwhelming to traditional farmers. Smart agriculture systems involve multiple components working together. Understanding these interactions requires new skills and knowledge.
Training programs help farmers adapt to new technology. Agricultural colleges and equipment suppliers offer comprehensive courses. These programs cover both technical operation and data interpretation.
User-friendly interfaces make systems more accessible. Modern software uses simple dashboards and clear graphics. Farmers don’t need technical backgrounds to operate smart agriculture systems.
Technical support services provide ongoing assistance. Equipment suppliers maintain help desks and field service teams. This support ensures farmers can resolve issues quickly and maintain productivity.
Data Management and Privacy
Smart agriculture generates enormous amounts of data. Managing this information effectively requires proper systems and procedures. Many farmers lack experience with data analysis and interpretation.
Cloud-based storage solutions simplify data management. These services automatically backup information and provide access from anywhere. Professional data analysis tools help identify important trends and patterns.
Data privacy concerns require careful attention. Farmers need assurance that sensitive business information remains confidential. Reputable technology providers implement strong security measures and clear privacy policies.
Data ownership rights must be clearly established. Farmers should retain control over information generated by their operations. Contracts should specify how data can be used and shared.
Future Trends in British Smart Agriculture
Artificial Intelligence Integration
Artificial intelligence is becoming increasingly important in smart agriculture. AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns humans might miss. These capabilities will revolutionize decision-making in British farming.
Machine learning algorithms improve over time. As they process more data, their predictions become more accurate. This continuous improvement makes smart agriculture systems increasingly valuable.
Automated decision-making will reduce farmer workload. AI systems will eventually make routine decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. Farmers will focus on strategic planning rather than daily operations.
Predictive analytics will prevent problems before they occur. AI systems will identify conditions likely to cause issues and recommend preventive actions. This proactive approach will improve both yields and sustainability.
Autonomous Farming Equipment
Self-driving tractors and harvesters are already operating on some British farms. These machines work 24 hours a day with incredible precision. Autonomous equipment will become standard on most farms within the next decade.
Swarm robotics involves multiple small robots working together. These systems can perform detailed tasks like weeding and harvesting delicate crops. Swarm robotics will enable precision farming at unprecedented scales.
Maintenance robots will service equipment automatically. These systems will perform routine checks, apply lubricants, and replace worn parts. Automated maintenance will reduce downtime and extend equipment life.
Safety improvements come from removing humans from dangerous operations. Autonomous equipment eliminates risks associated with heavy machinery operation. This technology will significantly reduce farming accidents.
Enhanced Connectivity Solutions
5G networks will transform data transmission capabilities. These high-speed connections will enable real-time video streaming and instant data analysis. Enhanced connectivity will support more sophisticated monitoring systems.
Satellite internet will reach remote farming areas. Low-orbit satellite constellations will provide reliable high-speed internet everywhere. This connectivity will ensure all British farms can access smart agriculture benefits.
Edge computing will process data locally. This approach reduces reliance on distant servers and improves response times. Local processing will enable instant decisions based on current conditions.
Blockchain technology will secure data transactions. This system will provide tamper-proof records of farming operations. Blockchain will support traceability requirements and organic certification processes.
Government Support and Policies
The British government strongly supports smart agriculture development. Various funding programs help farmers adopt new technologies. These initiatives recognize agriculture’s importance to the national economy and food security.
The Agriculture Bill includes provisions for technology adoption. Subsidies are shifting from land area payments to environmental and efficiency improvements. Smart agriculture practices qualify for many of these new support programs.
Research grants fund agricultural technology development. Universities and private companies receive funding to develop innovative solutions. This investment ensures Britain remains a leader in agricultural technology.
Regulatory frameworks support technology adoption while ensuring safety. Government agencies work with industry to develop appropriate standards. These regulations provide confidence for both farmers and technology providers.
Regional Success Stories
East Anglia: Arable Farming Revolution
East Anglia leads Britain in smart agriculture adoption. The region’s large-scale arable farms are perfect for precision farming techniques. Many farms have achieved remarkable efficiency improvements using IoT solutions.
One Norfolk farm reduced water usage by 40% using smart irrigation systems. Soil sensors provide real-time moisture data, triggering irrigation only when necessary. This precision has maintained yields while significantly reducing water costs.
Drone monitoring has transformed pest management across the region. Early detection allows targeted treatment, reducing pesticide usage by 30%. This approach protects beneficial insects while maintaining crop protection.
Automated machinery operates across thousands of acres with minimal supervision. GPS guidance ensures precise planting and harvesting patterns. These systems have reduced labor costs while improving operational efficiency.
Scotland: Livestock Innovation
Scottish farms excel in smart livestock management. Harsh weather conditions make traditional monitoring difficult, but IoT solutions provide continuous oversight regardless of conditions.
Highland cattle wearing smart collars provide location and health data. These systems prevent losses in challenging terrain and detect health issues early. Farmers can monitor entire herds from their smartphones.
Automated feeding systems adjust rations based on weather conditions and animal needs. During cold periods, animals receive additional energy-rich feed automatically. This precision nutrition improves animal welfare and productivity.
Milk quality monitoring provides instant feedback on dairy operations. Sensors detect changes in milk composition that indicate health or nutrition issues. Early intervention prevents problems from affecting entire herds.
Wales: Sustainable Hill Farming
Welsh hill farms use smart agriculture to maintain traditional practices while improving efficiency. IoT solutions help farmers manage challenging terrain and variable weather conditions.
Soil sensors monitor erosion and nutrient levels on steep slopes. This information guides sustainable grazing practices that protect soil health. Smart systems help balance animal needs with environmental protection.
Weather monitoring systems provide early warnings for extreme conditions. Farmers receive alerts about dangerous wind speeds or temperature drops. This advance notice allows protective measures for both animals and crops.
Remote monitoring reduces the need for daily visits to distant fields. Battery-powered sensors transmit data continuously, reducing fuel costs and vehicle wear. This efficiency is particularly valuable for extensive hill farming operations.
Looking Ahead: The Future of British Agriculture
Smart agriculture in Britain is still in its early stages. Current adoption represents only a fraction of the technology’s potential. The next decade will see dramatic expansion as costs continue falling and capabilities improve.
Integration between different systems will become seamless. Crop monitoring, livestock management, and equipment control will work together automatically. This integration will create truly intelligent farming operations.
Sustainability will drive continued innovation. Climate change concerns and environmental regulations will accelerate smart agriculture adoption. Technology will help farmers meet increasingly strict environmental standards.
Consumer demands for transparency will support traceability systems. Smart agriculture provides the detailed records consumers want about their food. This capability will become a competitive advantage for British farmers.
Conclusion
Smart agriculture in Britain represents a fundamental shift in farming practices. IoT solutions are helping farmers increase productivity while reducing environmental impact. This technology is not just changing how farming works – it’s ensuring British agriculture remains competitive and sustainable.
The benefits extend far beyond individual farms. Smart agriculture supports food security, environmental protection, and rural Economic development. As climate change and population growth create new challenges, these technologies provide essential solutions.
Success requires collaboration between farmers, technology providers, and government agencies. Continued investment in research, infrastructure, and training will ensure Britain maintains its leadership in agricultural innovation.
The future of British farming is smart, sustainable, and profitable. IoT solutions are making this future a reality today. Farmers who embrace these technologies will thrive in the changing agricultural landscape.
Smart agriculture in Britain is more than a technological upgrade – it’s a transformation that benefits farmers, consumers, and the environment. As this revolution continues, British agriculture will become more efficient, sustainable, and resilient than ever before.