Space exploration stands at the forefront of human endeavor, representing the relentless pursuit of knowledge and the quest to understand our place in the universe. From the earliest dreams of reaching the stars to the tangible achievements of modern space agencies and private companies, the journey into space has captivated the imagination of people worldwide.
Read More: SpaceX and Beyond: Exploring the Frontiers of Space Travel
Introduction to Space Travel
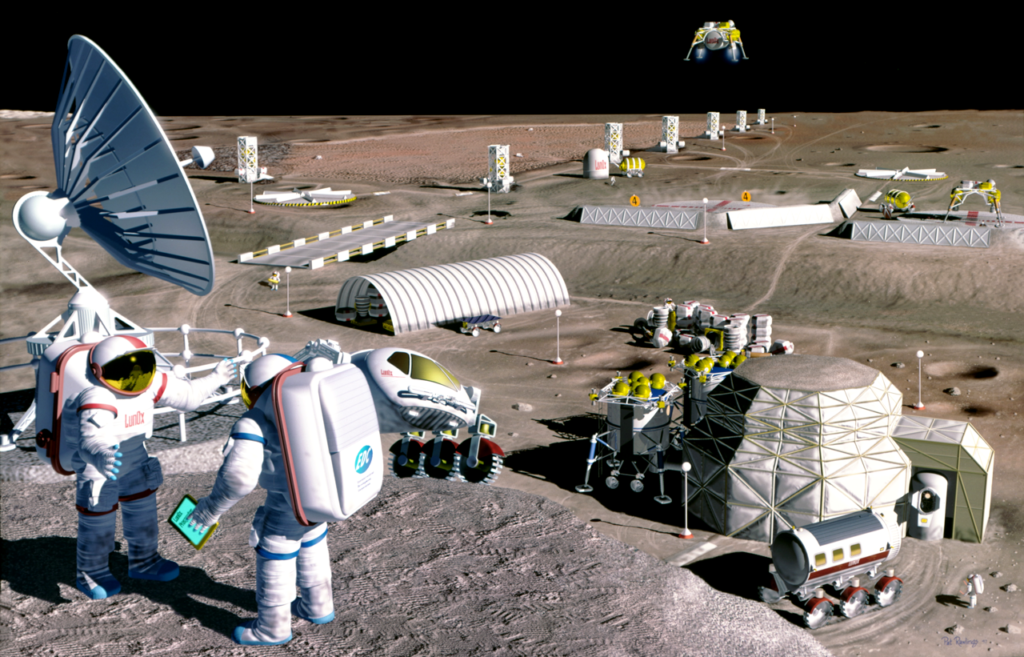
The concept of space travel has been ingrained in human culture for centuries, appearing in ancient myths and modern science fiction alike. However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that space exploration became a reality, driven by geopolitical rivalries and scientific curiosity.
Historic Milestones in Space Exploration
Early Space Exploration
The launch of the Soviet satellite Sputnik 1 in 1957 marked the dawn of the space age, triggering the space race between the United States and the Soviet Union. This period saw significant milestones, including the first human in space, Yuri Gagarin, aboard Vostok 1 in 1961.
Moon Landings
The crowning achievement of the space race came with NASA’s Apollo program, which culminated in the historic landing of Apollo 11 on the Moon in 1969. Neil Armstrong’s iconic words, “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind,” captured the imagination of millions around the world.
Space Shuttle Era
Following the Apollo missions, the space shuttle era ushered in a new era of space exploration, characterized by reusable spacecraft capable of carrying both astronauts and cargo to low Earth orbit. The space shuttle program enabled the construction of the International Space Station (ISS) and facilitated scientific research in microgravity.
Current State of Space Travel
International Space Station (ISS)
Since its launch in 1998, the ISS has served as a symbol of international cooperation in space, bringing together astronauts and scientists from around the world to conduct experiments in a unique microgravity environment. The ISS represents humanity’s ongoing presence in space and serves as a testbed for future long-duration missions.
Commercial Space Travel
In recent years, the landscape of space travel has been transformed by the emergence of commercial space companies like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic. These companies are pioneering new technologies and business models, with ambitions ranging from satellite deployment to lunar exploration and space tourism.
Mars Exploration
Mars has long captured the imagination of scientists and space enthusiasts as a potential destination for human exploration. Robotic missions like NASA’s Mars rovers have provided invaluable data about the Red Planet’s surface and atmosphere, laying the groundwork for future manned missions, such as NASA’s Artemis program.
Challenges and Risks
Technological Limitations
Despite remarkable advancements, space travel still faces numerous technical challenges, including propulsion systems capable of reaching distant destinations within reasonable timeframes, life support systems capable of sustaining astronauts for extended periods, and radiation protection to safeguard their health.
Health Risks for Astronauts
Extended exposure to the microgravity environment of space can have profound effects on the human body, including muscle atrophy, bone density loss, and cardiovascular issues. Additionally, the psychological challenges of isolation and confinement during long-duration missions present significant concerns for astronaut well-being.
Environmental Impact
The growing presence of satellites and space debris in Earth’s orbit poses risks to both current and future space missions. Collisions with debris fragments can damage spacecraft and generate more debris, exacerbating the problem in a phenomenon known as the Kessler syndrome. Addressing this issue is crucial for ensuring the sustainability of space exploration.
Future of Space Travel

Interplanetary Travel
As technology advances and scientific understanding grows, the prospect of human missions to other planets, such as Mars, becomes increasingly feasible. Interplanetary travel presents numerous challenges, including the development of propulsion systems capable of traversing vast distances and the design of habitats capable of supporting human life in hostile environments.
Space Tourism
The rise of commercial space companies has democratized access to space, offering civilians the opportunity to experience weightlessness and see the Earth from a new perspective. While space tourism remains prohibitively expensive for most people, ongoing innovation and competition in the industry hold promise for future affordability and accessibility.
Sustainable Space Exploration
Ensuring the long-term viability of human presence in space requires the development of sustainable technologies and practices. This includes renewable energy sources, recycling systems to minimize waste, and closed-loop life support systems capable of regenerating essential resources like water and oxygen.
Advancements in Space Technology
Propulsion Systems
Breakthroughs in propulsion technology, such as ion drives and nuclear propulsion, hold the potential to revolutionize space travel by enabling faster and more efficient means of reaching distant destinations within the solar system and beyond.
Space Habitats
Designing habitats capable of sustaining human life in the harsh environment of space is essential for enabling long-duration missions and future colonization efforts. These habitats must provide protection from radiation, temperature extremes, and micrometeoroid impacts while offering a comfortable living environment for astronauts.
Resource Utilization
Harnessing the resources found on other planets, such as water ice, and minerals, could reduce the cost and logistical challenges of space travel by enabling in-situ resource utilization. This approach could facilitate the establishment of self-sustaining colonies and pave the way for long-term human settlement beyond Earth.
Collaborative Efforts and Partnerships
International Cooperation
Space exploration has traditionally been a collaborative endeavor, with countries around the world pooling resources and expertise to achieve common goals. International cooperation fosters goodwill among nations and maximizes the scientific and technological benefits of space exploration for all humankind.
Public-Private Partnerships
The involvement of private companies in space exploration has brought fresh perspectives and resources to the industry, driving innovation and lowering the cost of access to space. Public-private partnerships enable governments to leverage the expertise and capabilities of the private sector while sharing the risks and rewards of space exploration.
Ethical Considerations

Space Debris Management
Mitigating the proliferation of space debris is essential for ensuring the safety of spacecraft and preventing collisions in Earth’s orbit. This requires coordinated efforts to track and catalog debris, develop debris removal technologies, and establish guidelines for responsible satellite deployment.
Planetary Protection
Preserving the integrity of other celestial bodies, such as Mars, is crucial for preventing contamination from Earth and safeguarding potential habitats for extraterrestrial life. Planetary protection protocols govern the sterilization of spacecraft and the avoidance of sensitive areas to minimize the risk of biological contamination.
Equity in Access to Space
Ensuring equitable access to space resources and opportunities is essential for promoting international cooperation and avoiding conflicts over space exploration. This includes addressing disparities in technological capabilities, financial resources, and regulatory frameworks to create a level playing field for all stakeholders.
Read More: Space Oddities: Unusual Phenomena in the Universe
FAQs
- How soon can we expect humans to travel to Mars? While plans for manned missions to Mars are in the works, logistical and technical challenges mean that it may be several decades before humans set foot on the Red Planet.
- What are the risks of space tourism? Space tourism poses various risks, including exposure to microgravity, radiation, and the potential for accidents during launch and re-entry.
- How does space exploration benefit life on Earth? Space exploration has led to numerous technological advancements and scientific discoveries with applications in medicine, telecommunications, and environmental monitoring.
- What measures are being taken to address space debris? Efforts to mitigate space debris include active debris removal missions, satellite tracking systems, and guidelines for responsible satellite deployment.
- Will space colonization ever become a reality? While challenges remain, ongoing research and technological development could one day make space colonization feasible, although it is likely to be a long-term endeavor.
The Final Words
As humanity stands on the brink of a new era in space exploration, the possibilities for our future beyond Earth are both exhilarating and daunting. By addressing the technical, ethical, and logistical challenges of space travel, we can pave the way for a more sustainable and inclusive future in the cosmos, where the wonders of the universe are within reach for all.